
Introduction
Knowing what file type to use and export with is important in every creative project. Certain file types are more suitable for certain situations and use cases, such as for print and for web. File-saving standards can also boost efficiency and reduce confusion, especially when working in teams that require frequent project-handoffs. This training will provide a base understanding of common file types, insight on what files to use for different scenarios, and recommendations for quality-retention in saving and exporting.
Through this training, you will also learn how to professionally deliver a final graphic design to the client, which includes how to create a style guide, how to export in different file formats, and how to package all files in a professional manner.’
Glossary
- Raster
- raster images are bitmaps of images, which is basically a bunch of individual pixels combined to create a whole image
- wide variety of hues mean it is best used for non-lined images, such as photographs, scanned artwork, or detailed graphics
- pixel-nature means they are more likely to lose quality when blown up
- cost less compared to vector graphics
- examples: BMP, TIF, GIF, JPG
- Vector:
- images are based on “paths” and mathematical formulas that define geometric shapes like lines, curves, polygons
- no color gradations, so better for flat images with uniform coloring
- can be scaled up or down with no quality loss
- cost more compared to raster graphics
- examples: SVG, EPS, PDF, AI
- dpi: dots per inch, print density of printers, we typically use 300 dpi
Common File Types
- PNG
- a format for storing raster images
- lossless data compression format
- ability to display transparent backgrounds
- JPG
- a format for storing raster images
- lossy compression method, which means redundant information is eliminated from the image through compression
- typically used for photographs and complex still images
- creates file size and image quality trade-off
- continuous editing and saving reduces image quality
- no ability to display transparent backgrounds
- PDF
- holds contents of a document in a fixed layout
- can contain fonts, images, text formats all in print ready format
- good file for sharing, particularly documents with text such as posters
- Good for creating “fillable” documents with text fields
- EPS
- Most common file format for vector documents
- Can also have bitmap images and text
- Does not preserve layers
- SVG
- Scalable Vector Graphics
- two-dimensional graphics file based on XML
- can be searched, indexed, scripted, and compressed
- accessible on both text editors and drawing software
- good for sharing graphics content over the internet
- Web designers often use this format to build a font into their pages and scale it dynamically based on the user’s browser
- TIF
- used to contain high quality graphics, especially for print
- Are not compressed, do not degrade when opened and edited
- holds both raster and vector based graphic data
- widely supported in image editing applications, so commonly used by graphic artists, photographers, and publishing authorities
- BMP
- bitmap image file
- contains raster graphics data which are independent of display devices, meaning they can be viewed without a graphics adapter
- generally uncompressed or compressed with a lossless compression method
- can store two-dimensional digital images with monochrome and color
- Work well with printers and CRTs
- Tend to be fairly big and bad with resizing
- GIF
- Graphics Interchange Format
- supports up to 8 bits per pixel in images which allows 256 different RGB colors to be used in a single image
- widely used for animated images
- also used for logos and images with sharp lines and edges
- uses lossless compression
- AI
- The Adobe Illustrator file
- Vector document
- Preserves layers
- OTF
- TTF
Use Case Decision Tree
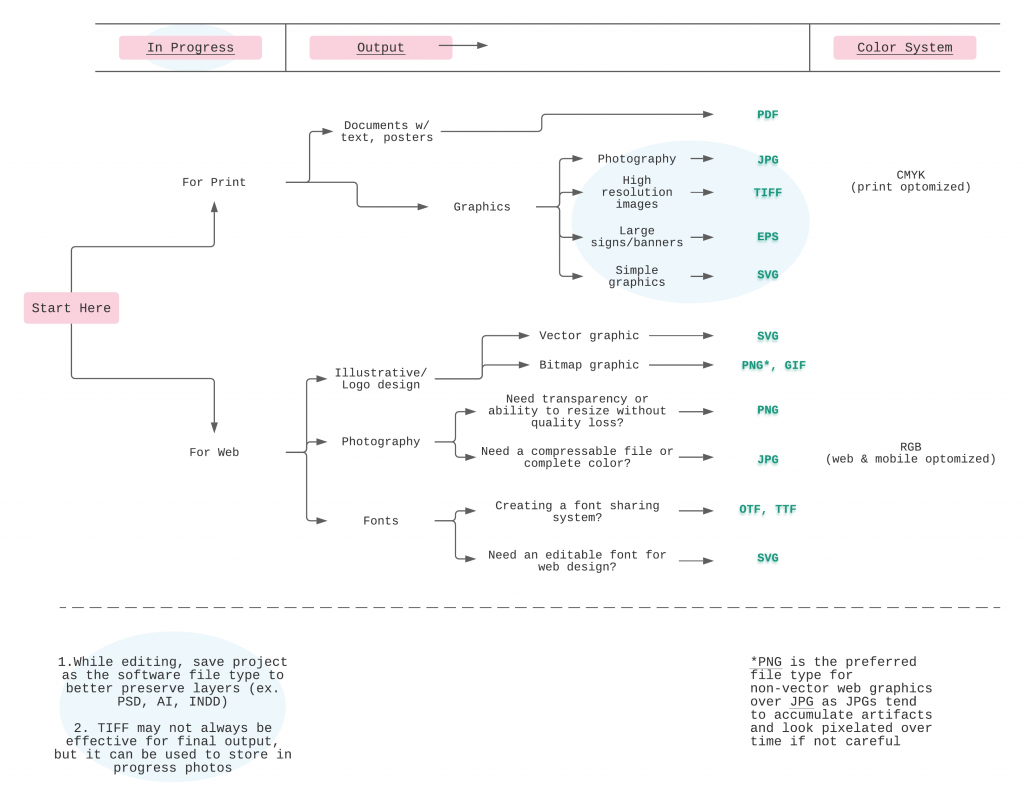
Export Method
- File > Save for Web (Legacy)
- gives more control over compression, previewing, and metadata
- can export a Photoshop video timeline as an animated GIF file
- File > Export As
- built with new code that developed upon the save for web (legacy) functionality
- good for making multiple copies of a PSD document at once, as PNG, JPEG, GIF, or SVG
- can handle larger documents
- can export multiple resolutions
- File > Export > Quick Export
- a faster version of the Export As command with fewer dialog box queries
- can be adjusted through File > Export > Export Preferences

Read on: Exporting Logos for Clients
