Frame 3
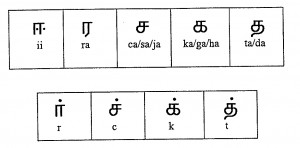
![]() (ii) In its production the lips are spread and the front of the tongue is raised as high as possible towards the hard palate without making any constriction. The tip of the tongue touches the lower part of the teeth. The vocal cords are vibrated during its production. The soft palate is raised. This is a high front un-rounded long vowel. This occurs in all positions in a word.
(ii) In its production the lips are spread and the front of the tongue is raised as high as possible towards the hard palate without making any constriction. The tip of the tongue touches the lower part of the teeth. The vocal cords are vibrated during its production. The soft palate is raised. This is a high front un-rounded long vowel. This occurs in all positions in a word.
![]() (r) The air escapes between the tip of the tongue and palate in its production. The soft palate is raised and the vocal cords are vibrated. This sound is described as the voiced alveolar flap. This occurs in all the positions in a word.
(r) The air escapes between the tip of the tongue and palate in its production. The soft palate is raised and the vocal cords are vibrated. This sound is described as the voiced alveolar flap. This occurs in all the positions in a word.
Compare the letters ![]() (ii) and
(ii) and ![]() (ra).
(ra). ![]() is formed by putting two dots on both sides of the third stroke and
is formed by putting two dots on both sides of the third stroke and ![]() (ra) is formed by adding a slightly angular short stroke as below. While writing
(ra) is formed by adding a slightly angular short stroke as below. While writing ![]() , it is written as
, it is written as ![]() but in print it will be
but in print it will be ![]() . But both are correct.
. But both are correct.
Compare the letters and copy three times.

We have seen earlier about ![]() and its production. As we have seen earlier this letter occurs in the word initial and medial positions. There are two sound values for this letter, namely voiced and voiceless. The one seen earlier described as voiceless (hard). The other one is voiced (soft). The movements of the speech organs are exactly the same as voiceless except for vibration of the vocal cords. It occurs initially in some of the borrowed words and medially after nasal as in
and its production. As we have seen earlier this letter occurs in the word initial and medial positions. There are two sound values for this letter, namely voiced and voiceless. The one seen earlier described as voiceless (hard). The other one is voiced (soft). The movements of the speech organs are exactly the same as voiceless except for vibration of the vocal cords. It occurs initially in some of the borrowed words and medially after nasal as in ![]() (pambaram). This may be described as a voiced bilabial stop sound.
(pambaram). This may be described as a voiced bilabial stop sound.
Read the Following words:

![]() (c) In its production the blade of the tongue touches the back portion of the alveolar ridge and the soft palate is raised. The blade of the tongue moves away from its position slowly. There is no vibration in the vocal cords. This is described as the voiceless palatal affricate. It occurs medially in modern Tamil as identical consonant cluster.
(c) In its production the blade of the tongue touches the back portion of the alveolar ridge and the soft palate is raised. The blade of the tongue moves away from its position slowly. There is no vibration in the vocal cords. This is described as the voiceless palatal affricate. It occurs medially in modern Tamil as identical consonant cluster.
![]() (k) The air stream is blocked by the back of the tongue while it is in firm contact with the soft palate in its production. The soft palate is in raised position so that no air escapes through the nasal cavity. The air comes out of the mouth with explosion when the back of the tongue is released suddenly. There is no vibration of the vocal cords during this production. This is voiceless velar stop. This occurs in the word initial and medial positions.
(k) The air stream is blocked by the back of the tongue while it is in firm contact with the soft palate in its production. The soft palate is in raised position so that no air escapes through the nasal cavity. The air comes out of the mouth with explosion when the back of the tongue is released suddenly. There is no vibration of the vocal cords during this production. This is voiceless velar stop. This occurs in the word initial and medial positions.
![]() (t) It is produced when the tip of the tongue touches the upper teeth. Here the soft palate is also raised so that the air con not escape through the nasal cavity. When the tip of the tongue is released from the upper teeth the air suddenly escapes through the mouth. There is no vibration in the vocal cords. This is a voiceless dental stop. It occurs initially and medially.
(t) It is produced when the tip of the tongue touches the upper teeth. Here the soft palate is also raised so that the air con not escape through the nasal cavity. When the tip of the tongue is released from the upper teeth the air suddenly escapes through the mouth. There is no vibration in the vocal cords. This is a voiceless dental stop. It occurs initially and medially.
Write the letters for (ca), (ka) and (ta):

In Tamil, each of the letter ![]() with or without secondary symbols for other vowels, have different pronunciation values depending upon the position in which they occur, or on the basis of letters with which they co-occur in a word.
with or without secondary symbols for other vowels, have different pronunciation values depending upon the position in which they occur, or on the basis of letters with which they co-occur in a word.
There are secondary symbols for each vowel. The vowels as such can used in the word initial position. In other places in a word corresponding secondary symbols are used. The secondary symbols may be added to the consonant either over the letter or before the primary letter or after the primary letter or both, before and after etc. The secondary symbols are introduced wherever the vowels are introduced. There are number of examples of vowel, consonant combinations are given for easy understanding of this concept.