Frame 13
In its production the tip of the tongue is made to contact the alveolar ridge. The soft palate is lowered and the air stream is pushed through the nasal cavity. The vocal cords are vibrated. The articulatory movements are exactly the same as those for the alveolar voiced stop ![]() . The only difference is in the case of the above sound represented by the letter
. The only difference is in the case of the above sound represented by the letter ![]() (n), the air is emitted through the nasal cavity. This is a voiced alveolar nasal. It occurs medially and finally.
(n), the air is emitted through the nasal cavity. This is a voiced alveolar nasal. It occurs medially and finally.
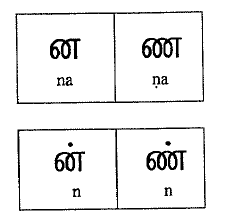
The letters ![]() and
and ![]() are different in pronounciation (Frame 5). The letters
are different in pronounciation (Frame 5). The letters ![]() etc., are always pronounced alveolar as in the English words, name, invitation etc.
etc., are always pronounced alveolar as in the English words, name, invitation etc. ![]() etc. can never occur in the beginning of a word. Only
etc. can never occur in the beginning of a word. Only ![]() and its series can occur in the word initial position. This is an important contrast between
and its series can occur in the word initial position. This is an important contrast between ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
Copy the letter for three times. (see Appendix I for hand-movements).

Read the words.

There is one more nasal with three loops shape![]() . In its production the tip of the tongue is curled and made to contact the roof of the mouth. The soft palate is lowered as in the production of other nasal and the air stream escapes freely through the nasal cavity. The vocal cords are vibration. This similar in production with
. In its production the tip of the tongue is curled and made to contact the roof of the mouth. The soft palate is lowered as in the production of other nasal and the air stream escapes freely through the nasal cavity. The vocal cords are vibration. This similar in production with ![]() except that the air stream is emitted through the nasal cavity. This may be described as a voiced retroflex nasal.
except that the air stream is emitted through the nasal cavity. This may be described as a voiced retroflex nasal.
This never occurs in the word initial position. Medially it occurs as a single consonant between vowels, as the first member of a consonant cluster, as the second member of a consonant cluster and in an identical consonant cluster.
Compare the letter for (na) with the letter for ![]() and write them three times each. Your letters should be similar to the ones at the extreme right(see Appendix I for hand-movements).
and write them three times each. Your letters should be similar to the ones at the extreme right(see Appendix I for hand-movements).

Observe how the secondary symbols for the vowels.


*The secondary symbol for the vowel, ![]() used in old Tamil is different from the modern Tamil for the consonants,
used in old Tamil is different from the modern Tamil for the consonants, ![]() and
and ![]() (see Chart III).
(see Chart III).
Also note the different secondary symbol for the vowel,![]() used for these two consonants(see Chart III).
used for these two consonants(see Chart III).
Read the following words.

