by Katie Kaufman Rogers
South by Southwest (SXSW)—a music, film, journalism, and tech festival held annually in Austin—came under fire last week for a decision to cancel a scheduled 2016 panel called “Level Up: Overcoming Harassment in Games,” as well as one other panel related to the gaming community. SXSW cited threats and harassment targeting the panel as its reason for canceling.
Since the cancellation, critiques have gone viral on Twitter, and major media outlets like BuzzFeed and Vox have threatened to pull out of SXSW altogether. Critics have described the cancellation as “clueless” at best and “craven” at worst. Some accuse the festival of “providing the blueprint for harassers and hatemongers.” Feeling the heat, festival organizers stated on Friday that they had “made a mistake” and outlined a new plan for a “day-long summit” on online harassment.
Some heralded this new event as a victory for anti-harassment activists. Former Texas State Senator Wendy Davis, for example, praised SXSW’s handling of the situation in a Facebook post:
This week, Austin’s SXSW faced well-deserved criticism after a decision-making misstep to cancel panels on women in gaming and digital harassment. In the last day, SXSW leadership have actively sought to correct course. People will make errors in judgement and will face consequences. It is important that we applaud when organizations realize their mistakes, and actively seek remedies. To that end, I gladly accepted an invitation to participate in the newly announced day-long Online Harassment Summit at SXSW. See you Austin to talk about how we must respect all people, all genders, in both the real world and the digital world. Thank you SXSW and all those who will be a part of this great new day!
However, not everyone is satisfied with this fix. For one, critics have pointed out that the new summit on harassment will include speakers who are affiliated with online harassment movements. “Level Up” panelists Katherine Cross, Caroline Sinders, and Randi Lee Harper say this raises serious “security concerns” for the summit. When Sinders expressed these concerns to SXSW, organizers responded by stating their commitment to preserving a “big tent” that encompasses a diversity of opinions. “If everyone shared the same viewpoint,” wrote SXSW, “that would make for a pretty boring event.”
Sinders stresses that any “big tent” has less to do with specific topics covered and more to do with creating a safe space for conversation. She argues that SXSW could have provided enhanced security for the “Level Up” panelists, instead of simply canceling their event. Others add that framing the situation as comprised of two parties with equally valid “ideas and opinions” implies that the issue of online harassment is something that is up for debate. Instead, they say, harassers give up their claims to credibility and legitimacy the moment they harass.
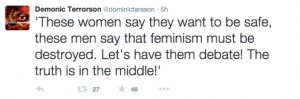
This heated response to issues of online harassment makes sense given recent controversies in the tech industry, particularly GamerGate, which has been consistently associated with the SXSW cancellations.
What is GamerGate?
In August 2014, an anonymous group of internet users began a coordinated and ongoing online harassment campaign against people—primarily women—who condemned sexism in the video game industry. This amorphous hate mob came to be associated with the Twitter hashtag #GamerGate. The movement targeted female video game developers, journalists, actresses, academic theorists, and other professionals and practitioners. The targets shared one thing in common: Feminism.
Online attacks have included rape threats, death threats, threats of mass shootings, and the creation of online flash games that allow players to beat up feminists who critique misogyny in video games. Many targets have also been doxed, meaning personal information like home addresses, phone numbers, employer information was found and publicly posted online. Doxing moves harassment offline, forcing several targets to flee their homes when violent, detailed threats showed up online alongside their addresses.
Self-identified members of GamerGate (called “GamerGaters” or “gators”) counter that their movement is not about harassment at all. They claim that harassers constitute a vocal minority. Instead, they define GamerGate as a movement about improving “ethical standards of video game journalism.” They accuse journalists of collusion with feminists and “social justice warriors,” saying these so-called conflicts of interest have contributed to a political correctness in game reviews.

Feminist game critics and their allies have widely questioned this “ethics” narrative, with many calling it a conspiracy theory. They argue that GamerGate’s true motivation is to police the boundaries of gaming culture—to exclude women, people of color, queer people, and transgender people and to silence their criticisms. They also contend that social media analytics data and the origins of the GamerGate movement show how this concern for “objectivity” and “ethical journalism” masks an effort to keep gaming as white, masculine, heterosexual, and cisgender as possible.
If this is indeed the case—if the root motivation of the GamerGate movement is white supremacism, heterosexism, cissexism, and misogyny rather than journalistic ethics—an obvious question follows: Who are these men, and why do they hate the people they see as outsiders?
Gender, Boundary Policing, and the “Gamer” Identity
Jeopardy! champion-turned-cultural-critic Arthur Chu describes GamerGate as follows:
Who are GamerGate? It’s one part entitled white guys claiming ownership over a subculture they feel is being invaded by outsiders. It’s one part entitled people who aren’t white guys who have, for one reason or another, made peace with being part of a white-guy-dominated culture and now enthusiastically join in trashing people who try to change it, for various complicated reasons. […] And it’s of course one part brazen opportunists with no prior interest in gaming seizing a chance to draw clicks while striking a blow against the left in the culture wars.
Here, Chu makes two points: (1) that gaming culture has historically been dominated by white men[i] and (2) that the harassment is less a result of GamerGaters’ sheer hatred of women than it is a violent defense of what they see as an existential threat to the “gamer” identity.
A number of journalists and feminists have described GamerGate as an outgrowth of a broader culture war about sexism and media, in which GamerGaters take issue with increasing racial and gender diversity in video games and in gaming culture. They say GamerGaters fear that this “bias” (read: writers calling for more diverse representation of characters in games) will change the games they love, the culture they identify with, and the social cohesion they depend on for feelings of belonging.
Katherine Cross, a feminist gaming critic and sociology PhD student at City University of New York (CUNY), posits that “GamerGate styles itself as a perverse kind of social justice movement for all gamers, constructing ‘gamer’ as an oppressed class unto itself.” Cross goes on to write that GamerGaters “claim to speak for the forgotten and bullied nerd, the outcast and misunderstood hobbyist who just wants to play video games yet is scapegoated for various and sundry evils.” On its face, this script makes logical sense: Raewyn Connell (1995) might conceive of “geek” or “gamer” masculinities as marginalized when compared to hegemonic masculinity, the dominant form of masculinity in society.
However, as Cross goes on to point out, “What this tidy narrative has always deliberately ignored is that all of GamerGate’s targets have been nerds and gamers.” That is, the very group of people that GamerGate purports to protect—gamers—include the very same people it attacks: women gamers.
If male gamers consistently considered women gamers to be genuine, authentic members of gaming culture, Cross’s point would clearly illuminate the contradictory logic of this narrative. But often times, they don’t. A common accusation levied against feminist gamers to undermine their criticisms is that they are not “real,” authentic gamers. For example, entire Reddit message boards, YouTube videos, and blog posts have been devoted to “outing” feminist gaming critic Anita Sarkeesian as an imposter. They aim to discredit her words by showing that she isn’t truly a gamer.
The popular trope of the fake geek girl offers another clear example of this. According to a CNN blog post by Joe Peacock, fake geek girls are “pretty girls pretending to be geeks for attention.” Peacock elaborates (emphases mine):
What I’m talking about is the girls who have no interest or history in gaming taking nearly naked photos of themselves with game controllers draped all over their body just to play at being a “model.” I get sick of wannabes who couldn’t make it as car show eye candy slapping on a Batman shirt and strutting around comic book conventions instead. I’m talking about an attention addict trying to satisfy her ego and feel pretty by infiltrating a community to seek the attention of guys she wouldn’t give the time of day on the street. […] I hate poachers. Pure and simple.
This definition of the fake geek girl is twofold, involving (1) a heightened performance of femininity and (2) cultural incompetence. For Peacock, fake geek girls have highly feminine, sexualized expressions of gender—they wear little clothing and “strut” around at comic cons. They are also “wannabes” who pretend to know about gaming to gain the attention of men, but really have little more than a superficial knowledge of the culture. The conflation of these two attributes in the fake geek girl trope exemplifies larger gender dynamics at play in gaming culture: incompetence is considered feminine. Thus, women must constantly perform their gaming knowledge to cast off the “fake” label and prove their authenticity as gamers.
Masculinities scholars (e.g. Pascoe 2007) observe similar processes in spaces where competence is considered masculine, which traps women in a double-bind: Expressing competence might afford women some legitimacy, but being taken seriously as a competent person means repudiating anything seen as feminine.
In a response to a critique of his original piece, Peacock adds (emphases mine):
For the record: I feel the same way about men who poach women. My wife is a marathoner (and I’ve even run one myself, and OH MY GOD I’ll never do that again). She participates in lots of female-specific events, like Iron Girl and the Nike Women’s Marathon. There are men who attend the expos and conferences for these events specifically to hit on women. I feel the same way about them. They’re gross.
Here, Peacock aims to prove his point—that he is an equal-opportunity despiser of cultural “poaching,” which he seems to understand as a hostile intrusion into a gendered social field[ii] by someone whose gender doesn’t belong. But for his comparison of gaming culture to women’s marathons to hold water, gaming would have to be analogous to a men’s-only marathon. Such a comparison reveals a belief that gaming culture is a fundamentally male space, designed to exist specifically and exclusively for men.
When Harassment Silences Discussion of Harassment
“Level Up” panelist Caroline Sinders says enhanced security would have made her feel safe enough to participate, but SXSW did not give her the chance to request it. To be fair, there is some precedent for opting for cancellation over risk of harm. Sarkeesian once cancelled a speaking engagement at Utah State University in light of a mass shooting threat. She had requested that metal detectors be used at entrances for the safety of attendees, but police declined to prohibit concealed weapons per state law.
Even so, SXSW’s navigation of this situation is confusing. GamerGate was one of the most widely covered, controversial tech debates of the past year. Given the mainstream media’s coverage of GamerGate (let alone the Twitter discussions), one might wonder how SXSW’s organizers could possibly not have anticipated such a response. It seems unbelievable that the organizers of an event billed as an “incubator of cutting-edge technologies” would be so out of touch as to not have anticipated backlash to a panel on online harassment.
Could providing additional security for the “Level Up” panel have been financially or logistically impossible? This seems unlikely. SXSW is staffed primarily by volunteers—not paid employees—and regularly features celebrities, some of whom almost certainly require beefed-up security. It seems reasonable to expect that enhanced security measures would be possible at SXSW, and so I wonder: why did the organizers cancel the panel without consulting a single panelist? Why was that decision made behind closed doors? And why is “online harassment” a justification to silence a discussion of that very subject? It could be that SXSW genuinely and naively miscalculated. But it could also be possible that the organizers knew exactly what they were doing—and they chose to reinforce the gendered boundaries of an industry to avoid rocking the boat.
[i] Extensive evidence has been documented in support of this argument, such as in the Feminist Frequency web series Tropes vs Women in Video Games and on the website Fat, Ugly, or Slutty.
[ii] The concept of the gendered field comes from feminist interpretations of Pierre Bourdieu’s (1990) theories of social reproduction (see Laberge 1995, McCall 1992, McNay 1999). Bourdieu (1990) conceives of social life as a series of games, simultaneously played out in a social landscape divided into collective spaces he calls social fields. Each field has its own set of rules and a particular hierarchical dynamic, wherein social actors compete to occupy dominant positions. A gendered field, then, is a field that is socially marked as masculine or feminine, thus benefiting participants who behave in ways that conform to the gendered coding of the field.
References
Bourdieu, Pierre. 1990. “Structure, Habitus, Practice.” Pp 52-66 in The Logic of Practice. Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press.
Connell, R.W. 1995. Masculinities. Berkeley, CA: University of California Press.
Pascoe, CJ. 2007. Dude, You’re a Fag: Masculinity and Sexuality in High School. Berkeley, CA: University of California Press.
Laberge, Suzanne. 1995. “Toward an Integration of Gender Into Bourdieu’s Concept of Cultural Capital.” Sociology of Sport Journal 12: 132–146.
McCall, Leslie. 1992. “Does gender fit? Bourdieu, feminism, and conceptions of social order.” Theory and Society 21: 837–867.
McNay, Lois. 1999. “Gender, habitus and the field: Pierre Bourdieu and the limits of reflexivity.” Theory, Culture, and Society 16 (1): 95–117.
Katie Kaufman Rogers is a PhD student in the Department of Sociology. Her research focuses on the areas of gender, race, and sexuality. You can follow her on Twitter at @katie_k_rogers.
