by Ori Swed
Upcoming presentation at Go-Betweens: Crossing Borders – An Interdisciplinary Conference at The University of Texas at Austin. Session B3: ‘Human Rights? Social Justice?‘ October 12, 2012. 3:40 – 5:20 pm. SAC 3.112
 Contemporary conflict areas and warzones across the globe witness the emergence of an old actor in a new face-the hired guns. As the quintessence of the spirit of capitalism in the battlefield, the new contractors’ companies take an increasing part in modern battlefields. From a pariah and symbol of cupidity the soldiers of fortune turned into businessmen in suits and million dollar companies, transformed from mercenaries into contractors. These contractors and companies proliferate in conflict areas, conducting various tasks as partners of governments and armies, from logistics and maintenance to intelligence and even actual fighting. In many battlefields they outnumbered the standing armies’ regular soldiers. This is the result of an historical process and an old arm wrestle between the market forces and political forces that tilt to one side or the other. Nevertheless, current trends evince these new characteristics. This differentiates them from former times and raises interesting questions on accountability, while challenging the Weberian notion on States and the monopoly of the legitimate use of violence.
Contemporary conflict areas and warzones across the globe witness the emergence of an old actor in a new face-the hired guns. As the quintessence of the spirit of capitalism in the battlefield, the new contractors’ companies take an increasing part in modern battlefields. From a pariah and symbol of cupidity the soldiers of fortune turned into businessmen in suits and million dollar companies, transformed from mercenaries into contractors. These contractors and companies proliferate in conflict areas, conducting various tasks as partners of governments and armies, from logistics and maintenance to intelligence and even actual fighting. In many battlefields they outnumbered the standing armies’ regular soldiers. This is the result of an historical process and an old arm wrestle between the market forces and political forces that tilt to one side or the other. Nevertheless, current trends evince these new characteristics. This differentiates them from former times and raises interesting questions on accountability, while challenging the Weberian notion on States and the monopoly of the legitimate use of violence.
Not so long ago, in the mid-90’s, mercenaries such as ‘Mad’ Mike Hoare, Bob Denard, ‘Black Jack’ Jean Schramme, Yair Klein, and many others prowled all across Africa and Latin America; following the committing “tradition” of Ernst von Mansfeld, Roger de Flor, Francesco Sforza and many other respectable names. These individuals, though many times operating under the advice and request of governments, were considered pariahs in international politics. Even the surprisingly successful intervention of the South African mercenary company Executive Outcomes (EO), which forced the notorious Revolutionary United Front that menaced Sierra Leone to ask for peace, was concluded with rapid banishment by the international community the moment EO harbored stabilization and democratic elections. In spite of the mitigating effect of EO presence on the Sierra Leone civil-war, (which was an arena the international community failed to deal with) no one in the international community could envision that hired-guns run the security and indirectly, the politics of a UN member.
The world, post 9/11, presented more than a few challenges for the international community and especially for the only world power, which was occupied with two distinct and distanced arenas about half the size of Texas. After a quick triumph in Iraq and Afghanistan came the phase of control and reconstruction for two turn countries with bad infrastructure and unstable politics, a phase which demanded further ‘boots on the ground’ than the over stretched and exhausted coalition could supply. The solution came in the form of outsourcing; outsourcing of control, construction, and if necessary, of fighting (Chatterjee 2009).
|
Table 1. Comparison of Contractor Personnel to Troop Levels (As of March 11) |
|
| Contractors Troops | Ratio |
| Afghanistan Only 90,339 99,800 | .91:1 |
| Iraq Only 64,253 45,660 | 1.41:1 |
| CENTCOM AOR 173,644 214,000 | .81:1 |
Source: CENTCOM 2nd Quarter FY 2011 Contractor Census Report; Troop data from Joint Chiefs of Staff, “Boots on the Ground” January report to Congress.
Notes: CENTCOM AOR includes figures for Afghanistan and Iraq. CENTCOM troop level adjusted by CRS to exclude troops deployed to non-Central Command locations (e.g., Djibouti, Philippines, Egypt). Troop levels for non-CENTCOM locations are from DMDC, DRS 11280, “Location Report” for June 2010.
Figure 1. Number of Contractor Personnel in Afghanistan vs. Troop Levels
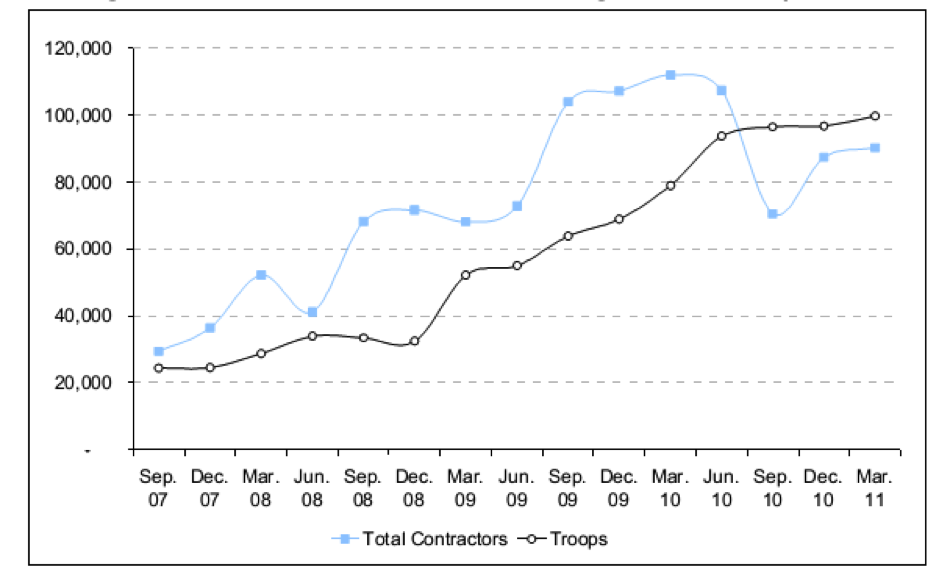 Source: CENTCOM Quarterly Census Reports; Troop Levels in the Afghan and Iraq Wars, FY2001-FY2012: Cost and Other Potential Issues, by Amy Belasco; Joint Staff, Joint Chiefs of Staff, “Boots on the Ground” monthly reports to Congress.
Source: CENTCOM Quarterly Census Reports; Troop Levels in the Afghan and Iraq Wars, FY2001-FY2012: Cost and Other Potential Issues, by Amy Belasco; Joint Staff, Joint Chiefs of Staff, “Boots on the Ground” monthly reports to Congress.
This rapid ‘makeover’, from pariah into mainstream political consensus, took less than a decade. At present, contractors or private military companies (PMC), are the providers of a variety of services starting in logistics and catering and ending with intelligence gathering, security and sometime even offense. Western companies are not the only players in the market and many other companies are taking their share in the “scramble for Iraq and Afghanistan”. Many of them are local, especially in Afghanistan.
Comparing major American conflicts from the last 250 years yields interesting results. The ratio of mercenaries/contractors and troops in the battlefield increased dramatically and shows record highs of 1:1. Historically this trend is new in the U.S context, though it has historical precedent for other nations.
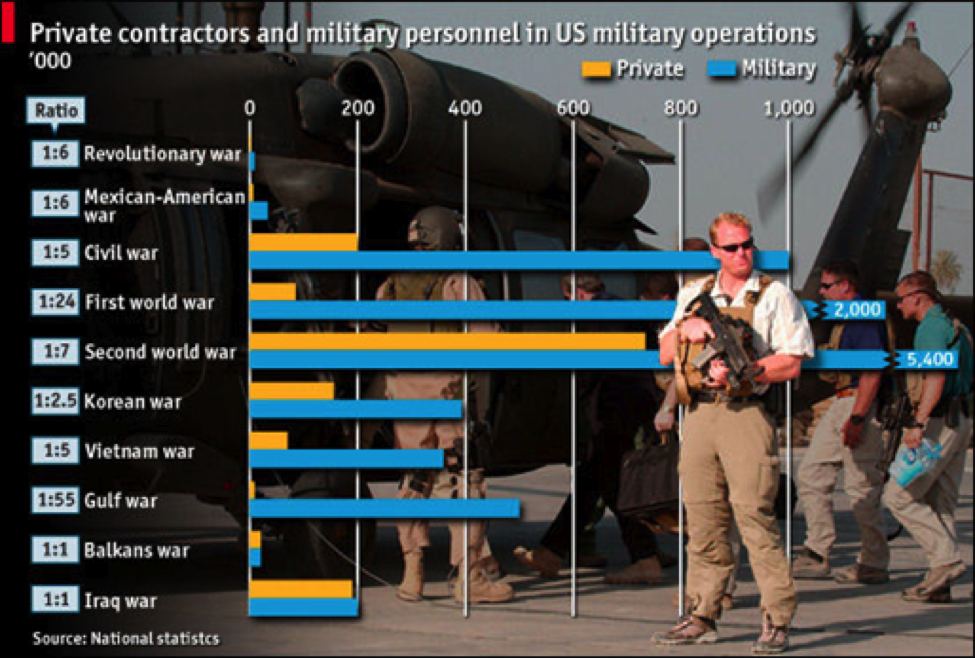 Source: http://www.economist.com/node/11955577?story_id=11955577
Source: http://www.economist.com/node/11955577?story_id=11955577
A ratio of 1:1 proposes that a significant military effort is conducted by contractors and not by military personnel. This trend raises points at issue over accountability and responsibility and questions the state’s ‘monopoly on the legitimate use of violence’. Take for example Blackwater, which retains a private navy, air force (it purchased recently a fleet of ‘Super Tucano’ turboprop fighting planes), and produces and sells its own armed personnel carrier- the Grizzly. Its capabilities surpass those of more than half of the UN members. Furthermore, in order to avoid the bad reputation associated with its activity in Iraq, the company rebranded its image and changed its name to Xe and later to Academi. Thus, we can see the dilemma of power and accountability (or problematic accountability) in the contractors’ contexts.
Currently, the interface between state/military and PMC’s is vast and not fully regulated. Problems occur frequently on the basis of determining jurisdiction and responsibility on the ground. Meanwhile contemporary warfare is changing as two distinct populations with different norms, characteristics, and organizational culture are working together, adding to an already complicated scenario.
