Emeritus Professors John Higley and UVA President Teresa Sullivan celebrating 100 years of Sociology at the University of Texas at Austin. Video of President Sullivan’s speech
Emeritus Professors John Higley and UVA President Teresa Sullivan celebrating 100 years of Sociology at the University of Texas at Austin. Video of President Sullivan’s speech
Category Archives: University of Texas at Austin Sociology
Amanda Stevenson on the Twitter chatter surrounding Texas HB2 and Wendy Davis’ Fillibuster

by Eric Enrique Borja
On September 12th, Amanda Stevenson was kind enough to discuss the work behind her recent paper in Contraception entitled, “Finding the Twitter users who stood with Wendy.” In the paper, Amanda examines Twitter chatter surrounding the Texas omnibus abortion restriction bill (Texas HB2) before, during and after Wendy Davis’ filibuster in summer 2013. The implications of Amanda’s results and conclusions are eloquently outlined both in the article published in Contraception, and her op-ed piece “Twitter analysis shows not all Texans want abortion rights limited,” which was published in the Houston Chronicle.
In this post I will only briefly go over some of the major takeaways from Amanda’s talk. I highly encourage you to read Amanda Stevenson’s articles for the full story.
1) “The Citizen’s Filibuster”
Amanda discussed one of the first major events in summer 2013, now referred to as the Citizen’s Filibuster. On June 20th, a special session of the Texas legislature was held. On the agenda was a pair of bills that would ban abortions after 20 weeks of pregnancy, restrict access to medication abortions and require abortion clinics to become ambulatory surgical care centers. In response to the special session abortion-rights groups such as: NARAL Pro-Choice Texas, Planned Parenthood, and the Lilith Fund, quickly organized a “citizen’s filibuster.” 
Approximately 700 people were organized in a flash, and the citizen’s filibuster was successful. Amanda showed that social media was important prior to Wendy Davis’ filibuster because it was instrumental in mobilizing people across the state of Texas.
2) Social media provided the primary coverage of Wendy Davis’ Filibuster
If it weren’t for the success of the Citizen’s Filibuster, Wendy Davis would have never had the opportunity to stage her filibuster. And if it were up to mainstream media outlets, the world would have never known what Wendy Davis had accomplished that day. Amanda discussed how mainstream media outlets failed to cover the filibuster. Therefore, social media became the primary source of coverage on Davis’ filibuster – with YouTube providing live streams for the world to see.
3) Social media data is generated through a selection process
Given the protocols that govern Twitter’s API, and the issues of access to technology, the kind of data a researcher pulls from social media is highly selective. Amanda was careful to point out that this does not mean social media data is useless, but that when you are interpreting your results you must be careful with what you think you are explaining. For Amanda, social media data is great at analyzing discussions that occur in social media, but falls short in accurately capturing public opinion. Interpreting social media data is like interpreting any kind of data a sociologist may collect; you have to take into consideration what and how much your data actually captures.
4) Hashtags can be a way to classify opinions
Trying to understand what people are attempting to convey through a tweet is a hard problem to resolve. One way this can be resolved, as illustrated by Amanda’s study, is to categorize tweets thematically using hashtags. For example, the hashtag “#standwithwendy” was a popular hashtag used through Davis’ filibuster. Users typically tag their tweets with hashtags to categorize them.
5) Social location estimates are inconclusive
In general, users do not GPS-enable their tweets. It’s been found that it is primarily younger males in urban areas who do. Therefore, to not further limit her sample, Amanda generated location estimates for users in her sample. Amanda writes, “For each account whose tweets had GPS data, I collected 100 tweets from the Twitter REST API v1.1. For all accounts, I collected location data from user profiles in the form of text strings.” By combining GPS data from GPS-enabled tweets and whatever location data she could garner from geocoded text string, Amanda was able to generate location estimates for more users than if she had solely relied on GPS data.
What impresses me the most about Amanda’s work is that she is careful (both in her talk and her paper) not to overreach in her conclusions. Moreover, her work is a great example of a project that elegantly employs qualitative and quantitative methodologies, something I aspire to achieve in my own work on social media. We all look forward to seeing more as Amanda’s dissertation develops.
UT Austin Sociology Centennial Celebration
The Sociology department at the University of Texas at Austin turned 100 this year, an event worthy of celebration. Many thanks to University of Virginia President, Dr. Teresa Sullivan (former Longhorn Vice Provost and proud Sociologist) for her talk on the future of Sociology and her help in launching our next 100 years. A video of our first 100 years can be found here.
UTAustinSOC party at ASA bringing together old friends and new
Brandon Andrew Robinson Writes for the HuffPost
Fourth year doctoral student, Brandon Andrew Robinson, writes for the HuffPost. Robinson’s piece is entitled, “Online Foreplay and Bringing Sexy Back.”
Excerpt from the piece:
Although the actual offline sexual encounters may not go according to the ways people discuss online, online foreplay can help lessen some of the fear or embarrassment of discussing sexuality, HIV, sexual practices and other aspects of one’s sex life. In a time of managing sexual risks, finding pleasurable and sexy approaches to discussing and experiencing one’s sexuality is important in order to counterbalance the now-common fear-driven approach to thinking and talking about sex.
To read the rest, follow this link: Online Foreplay and Bringing Sexy Back
#BlackTwitter/#BlackPolitics: the Lifeblood of a Community
by Eric Enrique Borja
This post is based on a larger paper I wrote for AFR/LAS 381: Black Radical Traditions.
_______________________________________________________________________________
In a stirring introduction to the multi-disk collection Voices of the Civil Rights Movement: Black American Freedom Songs, 1960-1966, the scholar, musician, and activist Bernice Johnson Reagon wrote that the “struggle for freedom” revealed “culture to be not luxury, not leisure, not entertainment, but the lifeblood of a community.” It was, she added, “the first time that I know the power of song to be an instrument for the articulation of our community concerns.”
– Ruth Feldstein, “I Don’t Trust You Anymore”: Nina Simone, Culture, and Black Activism in the 1960s.
hashtags like #DangerousBlackKids #solidarityisforwhitewomen #girlslikeus and more prompt INTERNATIONAL convos about real issues.
– Tweet by Franchesca Ramsey (@chescaleigh)
Over the past four years unprecedented large-scale movements have challenged states across the globe, and social media has been an important component in their development and articulation. With the advent of social media sites, such as Facebook and Twitter, people have the technological ability to instantaneously transcend space, time and resources (Aouraugh and Alexander 2011; Castells 2012; Earl and Kimport 2011; Eltantawy and Wiest 2011; Gerbaudo 2012; Hands 2011; Holmes 2012).
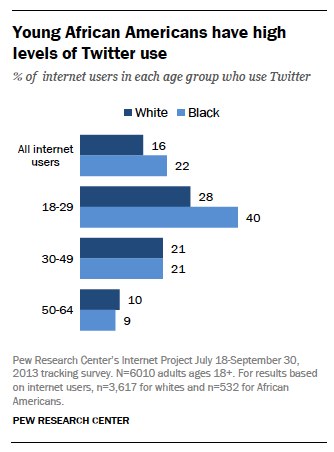
According to the World Bank, there are nearly 2.5 billion Internet users worldwide[i]. And according to Facebook’s Investor Relations site[ii] there are over a billion monthly active Facebook users. Furthermore, among African-Americans between the ages of 18-29 40% of them report using Twitter, which is much larger than the 28% of young whites who say they use it (Smith 2014).
The questions I explore in my research are: are we currently living in a historical moment where a new repertoire of contention is emerging? If so, how is social media changing the way we collectively contest for our interests? Therefore, my research focus has been political contention (Tilly 1986, 1995) – how “ordinary people[iii]” contend against the state for their collective interests. But it has been largely limited by how sociologists approach and define political contention. The course AFR/LAS 381: Black Radical Traditions with Dr. Minkah Makalani has expanded my understanding of political contention, reframing how I approach Tilly’s concept of a repertoire of contention.
Is Twitter the underground railroad of activism?
From Richard Iton’s (2008) book In Search of the Black Fantastic: Politics & Popular Culture in the Post-Civil Rights Era to Shana L. Redmond’s (2014) book Anthem: Social Movements and the Sound of Solidarity in the African Diaspora, we see a reframing of what it means to collectively contend against the state. Where Iton (2008, 2013), Redmond (2014) and many other scholars (Cohen 2004; Feldstein 2005; Griffin 2013; Neptune 2007; Sweet 2011) explore the cultural forms/protest tactics of music, literature, religion and dance, I argue the advent of social media in the 21st century has produced a new cultural form where Black politics is developed, expanded and rearticulated. I claim, in other words, that the cultural forms/protest tactics of music, literature, religion and dance constitute an old repertoire of contention, which is today being replaced by a new repertoire of contention that primarily utilizes social media, specifically hashtags (#). This is best illustrated by the social phenomenon popularly referred to as #BlackTwitter.
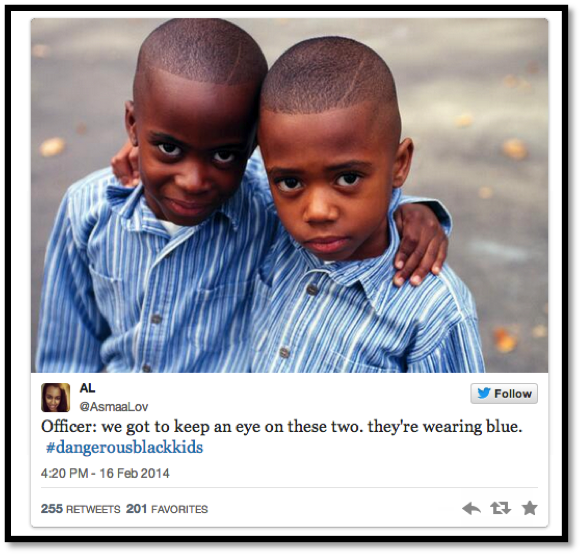
Adopting a similar understanding of the signifier “Black” that Redmond (2014) uses, “Black” is “a way to call attention to the overlapping projects of diaspora and racial formation that actively seek recognition in mutual struggle” (Redmond 2014:5). With this understanding of the signifier “Black” we can better understand the political potency of #BlackTwitter. In other words, the signifier “#BlackTwitter” refers to those users who are within the diaspora, and who actively articulate their political claims through the use of # such as #DangerousBlackKids, #DonLemonLogic, #girlslikeus and #solidarityisforwhitewomen, to name a few. I claim #BlackTwitter, similar to the Black anthems analyzed by Redmond (2014), “negotiate[s] and announce[s] the ambitions and claims of those whose very bodies [throw] into crisis the normativity of rules and liberties“ (Redmond 2014: 4).
The 21 Biggest #BlackTwitter Moments of 2013
The political potency of # for Black politics resides in the new space/time (Massey 2006) it creates. Which, in turn, fundamentally shifts the process of nation-ness (Anderson 2006) and marks a new phase in the mediazation of modern culture (Thompson 1991); two fundamental shifts comparable to the structural and cultural shifts that formed the modern repertoire of contention (Anderson 2006; Della Porta and Diani 1999; McAdam, Tarrow and Tilly 2001; Swidler 1986; Tarrow 1994; Tilly 1986, 1995; Young 2002).
Furthermore, it is important to keep in mind the unique historical position of Black people when working through Tilly’s concept of a repertoire of contention. Therefore, the new space/time created by the # also provides the place where Black culture and Black politics are rearticulated, forming a community that encompasses the Black diaspora.
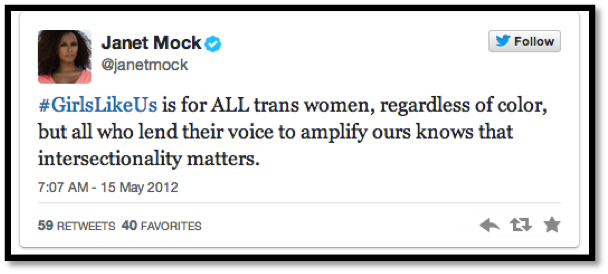
So similar to Redmond’s Black anthems, # “constitute differently configured diasporic formations that link people to one another through and beyond race into communities organized by imaginations of freedom from and an end to hierarchies of difference,” (Redmond 2014: 14). The # used by #BlackTwitter are the spaces where such communities are created – where the nation can be rearticulated, subverted, and transcended.
_______________________________________________________________________________
Works Cited
Anderson, Benedict. 2006. Imagined Communities. Brooklyn, NY: Verso.
Aouragh, Miriyam. 2011. The Egyptian Experience: Sense and Nonsense of the Internet Revolution. International Journal of Communication, 1344-1358.
Castells, Manuel. 2012. Networks of Outrage and Hope: Social Movements in the Internet Age. Malden, MA: Polity Press.
Cohen, Cathy J. 2004. “Deviance as Resistance: A New Research Agenda for the Study of Black Politics.” Du Bois Review, 1:1, 27-45.
Della Porta, Donatella and Mario Diani. 1999. Social Movements: An Introduction. Oxford, England: Blackwell Publishers.
Earl, Jennifer and Katrina Kimport. 2011. Digitally Enabled Social Change. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Eltantawy, Nahed and Julie B. Wiest. 2011. “Social Media in the Egyptian Revolution: Reconsidering Resource Mobilization.” International Journal of Communication, 1207-1224.
Feldstein, Ruth. 2005. “I Don’t Trust You Anymore’”: Nina Simone, Culture and Black Activism in the 1960s.” The Journal of American History, 1349-1379.
Gerbaudo, Paolo. 2012. Tweets and the Streets. London, UK: Pluto Press.
Griffin, Farah Jasmine. 2013. Harlem Nocturne: Women Artists & Progressive Politics During World War II. New York, NY: BasicCivitas Books.
Hands, Joss. 2011. @ is for Activism. London, UK: Pluto Press.
Holmes, Amy Austin. 2012. “There are Weeks When Decades Happen: Structure and Strategy in the Egyptian Revolution.” Mobilization: An International Journal 17:4, 391-410.
Iton, Richard. 2008. In Search of the Black Fantastic: Politics & Popular Culture in the Post-Civil Rights Era. Oxford, UK: Oxford Univerisity Press
Iton, Richard. 2013. “Still Life.” Small Axe, 40, 22-39.
Massey, Doreen. [2005] 2006. For Space. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications.
McAdam, Doug, Sydney Tarrow and Charles Tilly. 2001. Dynamics of Contention. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press.
Neptune, Harvey R. 2007. “Book Review: Caliban and the Yankees: Trinidad and the United States Occupation.” Caribbean Studies, 37:1, 310-314.
Redmond, Shana L. 2014. Anthem: Social Movements and the Sound of Solidarity in the African Diaspora. New York, NY: The New York University Press.
Smith, Aaron. 2014. African Americans and Technology Use: A Demographic Portrait. Pew Research Internet Project.
Sweet, James H. 2011. Domingos Álvares, African Healing, and the Intellectual History of the Atlantic World. Chapel Hill, NC: The University of North Carolina Press.
Swidler, Ann. 1986. “Culture in Action: Symbols and Strategies.” American Sociological Review, 51:2, 273-286.
Tarrow, Sydney. 1994. Power in Movement. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press.
Thompson, John B. 1990. Ideology and Modern Culture: Critical Social Theory in the Era of Mass Communication. Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press.
Tilly, Charles. 1986. The Contentious French. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
Tilly, Charles. [1995] 2005. Popular Contention in Great Britain 1758-1834. Boulder, CO: Paradigm Press
Young, Michael P. 2002. “Confessional Protest: The Religious Birth of U.S. National Social Movements.” American Sociological Review, 67:5, 660-688.
[iii] Tilly defines “ordinary people” as those who do not have access to the formal political mechanisms.
Esther Sullivan Writes for the London School of Economics American Politics and Policy Forum on Informal Homebuilding in Texas
Esther Sullivan discusses housing informality and self-help homebuilding in Texas in her recent post for the London School of Economics American Politics and Policy blog:
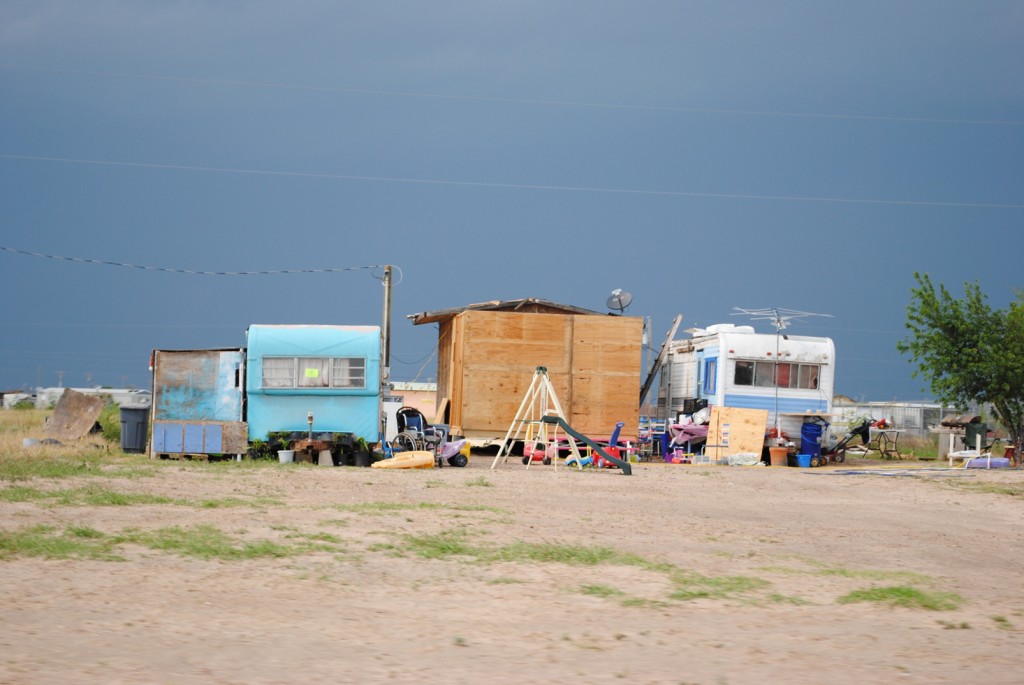
Owner self-building plays a crucial role in the production of affordable housing internationally and is widely recognized as a crucial source of housing production for the world’s poor. The concept of informal development has largely been relegated to settlements in developing countries despite its role in producing owner-occupied housing in the U.S. and in Europe, where self-provided housing accounts for over 50 percent of new housing production in countries such as the Netherlands, Ireland, Belgium and Germany…
The little research on informal homebuilding in the U.S. focuses primarily on the ways cities restrict such housing development and regulate informal development out of metropolitan areas. While these studies hypothesize that urban housing restrictions channel poor and immigrant populations to other cities or to rural hinterlands, our research shows instead that residents maintain economic ties to central cities while settling in county lands surrounding city centers where lax regulatory climates accommodate self-built, low-cost, informal housing.
Informal housing remains largely unstudied in the regions outside the U.S.-Mexico border and the communities where this housing is developed have thus not benefited from the policy interventions … To better understand the self-help housing stock found in informally developed communities we analyzed housing processes and housing conditions in two such communities in Central Texas.
Read the entire piece in the LSE APP here: http://bit.ly/1qCKS7B
There you can find a link to the entire article: “Informality on the urban periphery: Housing conditions and self-help strategies in Texas informal subdivisions” in Urban Studies.
Before You Know It: On LGBT Aging
by Kathy Hill
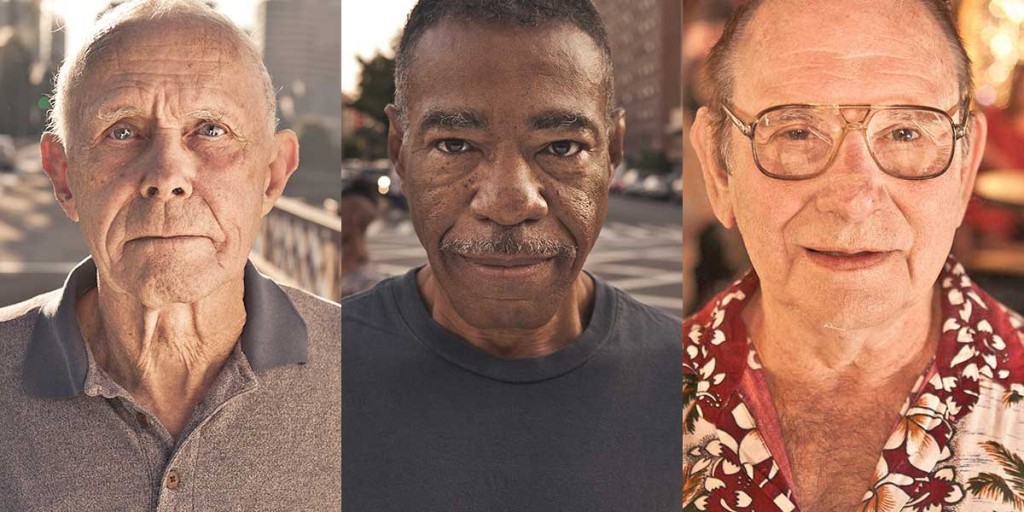
Before You Know It is an award-winning 2014 documentary film directed and produced by PJ Raval, an Austin local and assistant professor in the RTF Department at UT Austin. It premiered at the 2013 SXSW and showed at the Violet Crown Cinema this summer. In this film, Raval documents the lives of three gay seniors – their challenges, adventures, and their relationships.
Ty is an LGBT activist from Harlem, New York. Though he is in his 60’s, his passion for gay rights and hope for his own marriage is youthful. He is skeptical, but happily surprised when his advocacy for SAGE, Services and Advocacy for GLBT Elders, is received well in the Harlem community. Ty is enthusiastic when gay marriage passes in New York. He is eager to serve as the best man for his best friend’s wedding, and he won’t stop asking his partner about their own potential marriage. Ty’s starry-eyed hope is confirmation that you’re never too old to dream of love and marriage.
Robert the “Mouth of the South” is a feisty bar owner in Galveston, TX. Robert’s Lafitte is a welcome stage for drag queens in Galveston and home to many of the LGBT community there. They hold Thanksgiving dinners and life commemorations of drag queens and friends who have passed on and “moved to California,” as Robert warmly puts it. Robert struggles to feel well as he deals with a lawsuit for which he might lose the bar, but his LGBT family keeps the spirit of the bar alive with the continuing of drag performances and festive gatherings.
Dennis is a soft-spoken and kind-hearted widower who lives in Niceville, FL. After his wife died, he began to explore his sexual identity and started dressing in women’s clothing under the name “Dee.” Dennis takes trips to Portland, Oregon where he lives in an LGBT retirement home and explores online dating, gay bars, and even goes on a gay cruise. At the age of 70, Dennis is not afraid to try something different and new. Dennis lives a solitary life in a small old house when he goes back to Niceville. One day, he comes back from Portland to find his house covered in mold. He walks away from the only home he’s ever owned, all of his material possessions and memories. For me, Dennis’s story was the most inspiring; he shows us that self-discovery happens can happened at any age.
“Before You Know It” is about aging, yet it will make you feel more alive as you watch and listen to each person’s story. Robert’s “Mahna mahna” drag performance made me laugh hysterically. Ty, always asking his partner about marriage, made me blush. And Dennis’s bravery, as zipped up his hot pink go-go boots and walked around the gay cruise ship alone, made me cringe with fear, and then, sigh with admiration. Each story is a reminder that hope for love, discovery of self, and passion for change can happen at any stage of life. “Before You Know It” shows the life as a learning process, specifically in the lives of three gay seniors, but also in a way that relates all people, old or young. We continue to learn more about ourselves and how we can connect with our social world, and that doesn’t stop when we get older.
PJ Raval is named one of the Out Magazine’s “Out 100 2010” and Filmmaker Magazine’s “25 new faces of independent film 2006.” His credits include “Trinidad” (Showtime) and The Christeene video collection (SXSW). Raval’s cinematography work includes Academy Award-nominated “Trouble The Water” and “Bounceback” (SWSX 2013).
Watch the trailer of “Before You Know It” and be sure to catch the film the next time you can:
Twitter analysis shows not all Texans want abortion rights limited
Social media analysis challenges stereotype of conservative state
By Amanda Jean Stevenson
The full text of the article is available at this link to the June 24th edition of The Houston Chronicle
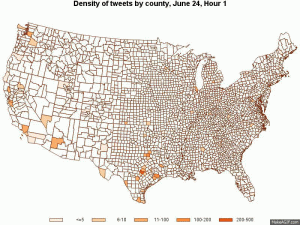
One year ago this week, state Sen. Wendy Davis drew national attention with her filibuster of HB2, an omnibus abortion restriction bill that has since ushered in a 50 percent decline in the number of abortion clinics in our state. For 11 hours a year ago today, she stood on the floor of the Texas Senate in her pink running shoes as thousands of Texans rallied around her at the state Capitol and 180,000 people watched online. Her filibuster also sparked the wildly popular social media hashtag #StandWithWendy, instantly offering insight into a segment of the state that isn’t so red: Not all Texans agree that restricting abortion rights is a good idea.
Most discussion of Texas in the national media focuses on the state’s extremely conservative factions. But Texas is full of principled people across the political spectrum. Thousands of them marched on the state Capitol to oppose HB2. Before Davis filibustered, 700 people registered to testify in a “citizens filibuster” that lasted late into the night of June 20, and thousands filled Capitol buildings day after day dressed in orange T-shirts, the color chosen to symbolize the fight against HB2. After Davis’ filibuster, 19,000 filed comments against the bill and they continued to fill the Capitol for each hearing and vote. Throughout, they were joined by a digital chorus on Twitter that was hundreds of thousands strong.
I have analyzed the 1.66 million tweets that comprise the Twitter discussion associated with the bill. These tweets came from 399,000 users worldwide. Roughly 44 percent of the tweets were sent from Texans in support of abortion rights, and in all, about 115,500 Texans expressed their support for abortion rights as part of the Twitter discussion of the bill. These Texans are not all Austin liberals. They live throughout the state, in rural and urban areas. In fact, tweets in support of the filibuster were sent from 189 of Texas’ 254 counties, including the majority of rural counties and all urban ones. Only 1.8 percent of the Texas population lives in counties from which no identifiable tweets of support were sent.
How I Make You Invisible
by Mario Venegas
Introduction
The play Am I Invisible engages audiences through a series of performances that demonstrate the perspective of the homeless in Austin, Texas. Directed by Roni Chelben, the presentation consists of video footage of interviews with members of homeless communities, followed by a series of monologues, and ends with a Forum Theater scene (Boal 1975). The monologues and interviews portray the lived experiences of members of the Austin homeless community. Some of these monologues include poetry, song, and personal testimonies of being ignored and made socially invisible in the consumption-laden streets of Austin. During the performance, I had my own preconceptions about what would take place and how the piece might be just another form of entertainment or ‘poverty porn.’ I was torn between these critical streams of thought and my own personal experiences in organizing street theater and productions like the Tunnel of Oppression back when I was an undergrad. However, once the play was over, and I was able to go home, rest and process, I started making better sense of Chelben’s production.
The Forum Theater is especially interesting. In Chelben’s performance spectators witness a story of a man’s ‘descent’ into homelessness. In the scene, the man gets no help from his family or friends to move his stuff from an apartment whose rent is long overdue. He ends up homeless and seeks help at a shelter, but the facility is too full. So he meets another homeless man at the facility, and they both sleep in a public space, where they’re then harassed by the police. The scene ends with both men being arrested for resisting authority.
After the scene takes place, Chelben, who is the facilitator or ‘joker’ (Boal 1975; Schutzman et al 2006), guides the audience to engage with the scene, which is then reenacted according to suggestions made by audience members. The audience has a chance to talk among themselves and propose actions that could change the outcome of the scene. The goal to implement the suggestions in order to spark dialogues among the audience and cast on the social issues presented.
I want to share some of my thoughts on the performance below. I’m relying partly on the works of Augusto Boal, such as Theatre of the Oppressed (1975), and other related perspectives. Also, I’m speaking from a spectator’s point of view, specifically that of a graduate student with limited knowledge of the production itself and of being homeless.
Theatre of the Oppressed
Theatre of the Oppressed talks about ways in which theater has become a tool of the ruling classes; confined to a bourgeois space that is divorced from the social and political spheres of life (Boal 1975, p 77). Inspired by Paulo Freire’s Pedagogy of the Oppressed, Boal suggests, and demonstrates in his work, techniques to transform audiences from a passive role to an active one; making them constitutive of the theatrical process of social conscientização.
One such technique is the use of Forum Theater. Forum Theater is where ‘spec-actors’ give input on a scene in order to change its course of action within the bounds of the social context so that realistic solutions are discussed and rehearsed. The goal of Boal’s work is to use theater as a means to empower audiences by creating a space to ‘practice’ social change. Of interest here is the use of the spec-actor as a means to locate the participatory potential of audiences in Am I Invisible.
During the entire production, two things stood out to me. The first thing that struck me was the monologues of being invisible in Austin. I admit I, too, am guilty of participating in this ‘invisibilization’ process as I meander through downtown. When a homeless person asks me for spare change or tries to get my attention, I shake my head, look down and just keep on walking. Why do I react in this way? What has conditioned me to not only ignore but also deny any sort of assistance to a homeless person? I’ll return to these questions later.
A second aspect of the production that stood out to me was the use of the Forum Theater in the final scene. After the first run-through of how the man became homeless, audience members were allowed to contribute to the scene and try to change its outcome. However, the ‘joker’ or facilitator does not allow for easy, magical solutions—i.e. a friend suddenly appearing or winning the lottery. The suggestions must be realistic and feasible within the context of the scene. According to Boal, the idea behind this practice is for audiences to rehearse their suggestions as a way to develop a sense of social and political participation.
Boal (1975) writes:
Often a person is very revolutionary when in a public forum he envisages and advocates revolutionary and heroic acts; on the other hand, he often realizes that things are not so easy when he himself has to practice what he suggests.
The theater provides a ‘play space’ for these types of rehearsals, but again, not without faults to be addressed in another discussion.
To go back to my previous questions, I wished we could have had a conversation about the ways in which those of us who are not homeless are implicated in the process of invisibilizing the homeless. I think this aspect was underdeveloped and would’ve provided a more engaging conversation. That is, it would be fruitful to use Boal’s techniques to illuminate the ways images are used to police boundaries between groups, viz the homed versus the homeless. In other words, to incorporate into the discussion some ways in which images of the homeless and the poor are part of a discourse of class and social degeneration used to police the boundaries between classes (McClintock 1994, p 47) to further marginalize the poor, as in this commercial.
Conclusion
It was through applied theater that my sociological imagination was first sparked. Community theater gives me a space for a queer marginalized body on a white campus to survive and to develop a means and a language to navigate the prisms of inequality and power we inhabit. I believe applied theater is fertile grounds for sociological engagement and provides one of many ways to communicate an understanding of social structures. Overall, I found Am I Invisible to be a rich play.
Here is a site where audiences can submit comments as part of a journal project: http://invisibleinaustin.com/journal/
References
Boal, Augusto. (1979) Theatre of the Oppressed. New York, NY: Urizen Books.
Fraser, Nancy (1995) “From Redistribution to Recognition? Dilemmas of Justice in a ‘Post-Socialist’ Age” New Left Review 212: 68-93.
Fraser, Nancy & Naples, Nancy A. (2004) “To Interpret the World and to Change it: An Interview with Nancy Fraser” Signs 29(4): 1103-1124.
Meikle, Glendora. (2013) “Poverty porn: is sensationalism justified if it helps those in need?” The Guardian accessed May 1, 2014 at (http://www.theguardian.com/global-development-professionals-network/2013/jul/05/poverty-porn-development-reporting-fistula).
McClintock, Anne. (1995) Imperial Leather: Race, Gender, and Sexuality in the Colonial Contest. New York, NY: Routledge.
Neelands, Jonathan. (2007) “Taming the political: the struggle over recognition in the politics of applied theatre” Research in Drama Education 12(3): 305-317.
Schutzman, Mady (1994) “Brechtian Shamanism: The Political Therapy of Augusto Boal” p. 137-155 in Playing Boal: Theatre, therapy, activism edited by Mady Schutzman and Jan Cohen-Cruz. New York, NY: Routledge.